The Evolution of Art Techniques
Art techniques have evolved significantly, transforming from traditional methods to digital platforms. Historically, artists relied heavily on physical materials like canvas, paint, and brushes. For centuries, techniques such as oil painting, watercolor, and charcoal drawing dominated the art scene. Frescoes and mosaics were prevalent in ancient times, showcasing the technical skill of artists in complex mediums.
In the mid-20th century, advancements in technology began influencing artistic practices. The introduction of photography altered how artists approached realism and abstraction. Artists started integrating mixed media into their works, blending traditional materials with unconventional items like fabric or found objects. This period marked the beginning of a shift towards more experimental art forms.
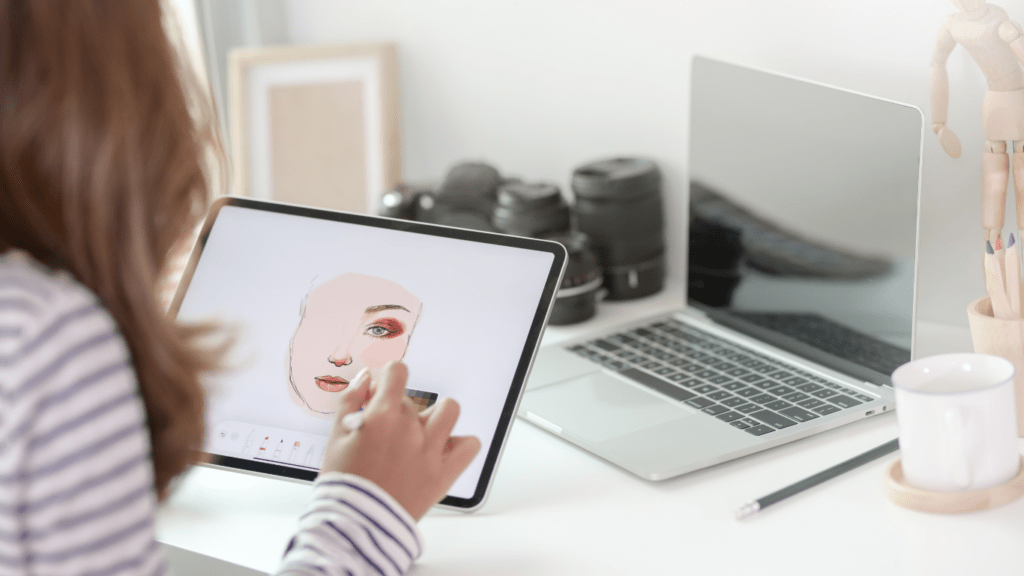
In recent decades, digital art has surged in popularity, bridging the gap between traditional and modern techniques. Software programs like Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, and Corel Painter provide artists with tools that replicate the textures and effects of physical mediums. Graphic tablets and styluses have become essential for digital artists, enabling precision and versatility in their creations.
Today, artists can merge traditional and digital methods seamlessly. Hybrid art forms, such as digital painting over a watercolor base or the use of scanned sketches combined with digital enhancements, have emerged. This blending allows artists to harness the strengths of both approaches, creating unique and innovative works. Digital platforms also offer the advantage of iterative development, where artists can revise and refine their work without degrading the original.
The evolution of art techniques demonstrates a dynamic interplay between tradition and innovation. By adapting new technologies, artists continue to expand the boundaries of their craft, exploring new possibilities while honoring historical practices.
Traditional Art Techniques
Traditional art techniques provide the foundation for many digital innovations. These methods form the core principles behind artistic practices, ensuring a seamless transition into digital platforms.
Classical Methods
Classical methods include drawing (charcoal, pencils), painting (oil, watercolor), and sculpting (clay, stone). These techniques highlight the use of tangible materials, requiring skill and precision.
- Drawing: Artists use charcoal and pencils for sketching. These tools offer different textures and shades.
- Painting: Oil and watercolor paints provide unique blending capabilities. Each medium has distinct drying times and textures.
- Sculpting: Using clay and stone, sculptors create three-dimensional art. This method demands physical interaction with the material.
Renowned Traditional Artists
Renowned traditional artists have set timeless standards. Their work influences both traditional and digital mediums.
- Leonardo da Vinci: Known for “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper,” Da Vinci’s precision and detail continue to inspire modern techniques.
- Michelangelo: His sculptures, like “David” and the Sistine Chapel ceiling, showcase his mastery of form and anatomy.
- Pablo Picasso: Transitioning from traditional techniques to pioneering Cubism, Picasso’s evolution impacts both modern art and digital interpretations.
Traditional art methods continue to shape and influence the dynamic interplay between historical practices and modern innovations.
The Rise of Digital Art

Digital art has emerged as a transformative medium, blending traditional techniques with modern technology. This evolution has opened new avenues for artistic expression.
Early Developments
Early developments in digital art date back to the 1960s. Artists began using computers to create geometric patterns and simple graphics. Ivan Sutherland’s Sketchpad, developed in 1963, was a pioneering tool allowing users to draw directly onto a computer screen. It set the stage for later advancements by providing a digital canvas for artists.
The 1980s and 1990s saw significant progress in digital art tools. Software like Adobe Photoshop, introduced in 1988, revolutionized the way artists manipulated images. The accessibility of personal computers further facilitated the growth of digital art. Artists could now experiment with new styles and techniques without the limitations of physical materials.
Types of Digital Art
Digital art encompasses various forms, each utilizing technology in unique ways. Examples include digital painting, 3D modeling, and vector art.
- Digital Painting: Artists use software like Corel Painter and Procreate to simulate traditional painting techniques. Brushes, colors, and textures mimic those used in oil, watercolor, and acrylic painting.
- 3D Modeling: This type involves creating three-dimensional objects using software such as Blender or Autodesk Maya. Artists can render these models for use in animation, video games, and virtual reality experiences.
- Vector Art: Artists create this type using mathematics-based software like Adobe Illustrator. Vector art is ideal for scalable designs, making it popular in graphic design and print media.
Each type of digital art offers unique advantages, expanding the possibilities for creative expression and bridging the gap between traditional and modern techniques.
Bridging the Gap: Digital Meets Traditional
The integration of digital and traditional art techniques creates a rich tapestry of creative possibilities. Artists now blend methods, tools, and approaches from both realms to produce unprecedented works.
Hybrid Techniques
Hybrid techniques merge traditional and digital art methods. For example, artists might start with hand-drawn sketches and then enhance them digitally using software like Adobe Illustrator. This combination allows the intricate detail of traditional methods to meet the versatility of digital tools. Moreover, digital painting apps like Procreate offer brushes that mimic real-world textures, allowing seamless transitions between traditional and digital styles.
Tool Integration
Tool integration involves using both traditional and digital tools in the creation process. For instance, a traditional artist may use a tablet to sketch initial ideas or refine details digitally. Hardware like Wacom tablets and styluses is designed to replicate the experience of drawing on paper. Software like Corel Painter replicates the look and feel of natural media, enabling artists to combine physical brushstrokes with digital enhancements effortlessly.
Case Studies and Examples
Several renowned artists exemplify the effective integration of traditional and digital techniques. For example, artist Kyle T. Webster blends watercolor techniques with Photoshop brushes to create lifelike illustrations. Another notable instance is the work of Loish, who combines hand-drawn elements and digital coloring to produce captivating character designs. These examples show how artists leverage both realms to push creative boundaries.
The Impact on Artists and Audiences
Digital art has created profound changes for both creators and viewers. Its influence extends to skill development and accessibility.
Skill Development
Artists often experience accelerated learning due to digital tools. Software like Corel Painter and Clip Studio Paint offer features such as undo options, layers, and digital brushes, enabling rapid experimentation and mastery without material waste. Hybrid techniques enrich artists’ portfolios, providing versatility and adaptability in various media. For example, an artist might start with traditional sketches, then refine details digitally, creating a piece that showcases expertise in both domains.
Accessibility and Exposure
Digital platforms improve accessibility and exposure for artists. Tools like tablets and styluses have democratized art creation, making it easier for individuals regardless of background or financial status to produce professional-quality work. Online galleries and social networks, including platforms like:
- DeviantArt
- ArtStation
provide global exposure, leveling the playing field. Artists can reach diverse audiences, gain feedback, and build communities around their work, significantly broadening their opportunities for recognition and commercial success.
Future of Art Techniques
Digital art continues evolving, blending traditional methods with modern technology. This section explores innovations and predictions that will shape the future.
Innovations to Watch
Several innovations are set to redefine art techniques. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are creating immersive experiences. AR overlays digital elements on real-world environments, while VR completely submerges users in a digital space. Both offer new dimensions for artists to explore.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another significant innovation. AI tools assist artists by generating ideas, streamlining workflows, and even creating art independently. Programs like DALL-E and DeepArt harness deep learning algorithms to produce unique artworks based on user inputs.
3D printing is also making a considerable impact. Artists can now transform digital models into physical sculptures with precision and ease. This technology bridges the gap between digital and physical art, expanding creative possibilities.
Predictions for the Art World
- Art techniques will continue integrating digital and traditional elements. Artists will use hybrid methods, combining hand-drawn sketches with digital enhancements. These techniques will produce more versatile and dynamic works.
- The rise of NFTs (non-fungible tokens) will revolutionize how art is bought and sold. Artists tokenize their work, enabling direct sales and ownership transfer on blockchain platforms. This trend will offer new revenue streams for digital artists.
- Educational institutions will incorporate more digital tools into their curricula. Students will learn both classical and modern techniques, preparing them for an ever-evolving art landscape. Programs like Adobe Creative Suite and Blender will become standard in art education.
- Online platforms will further democratize art creation and exposure. Artists will reach global audiences, gain feedback, and build communities more easily. Social media and virtual galleries will continue playing crucial roles in artist recognition.
These innovations and trends indicate a future where digital and traditional art techniques coexist and flourish, enriching the art world for artists and audiences alike.