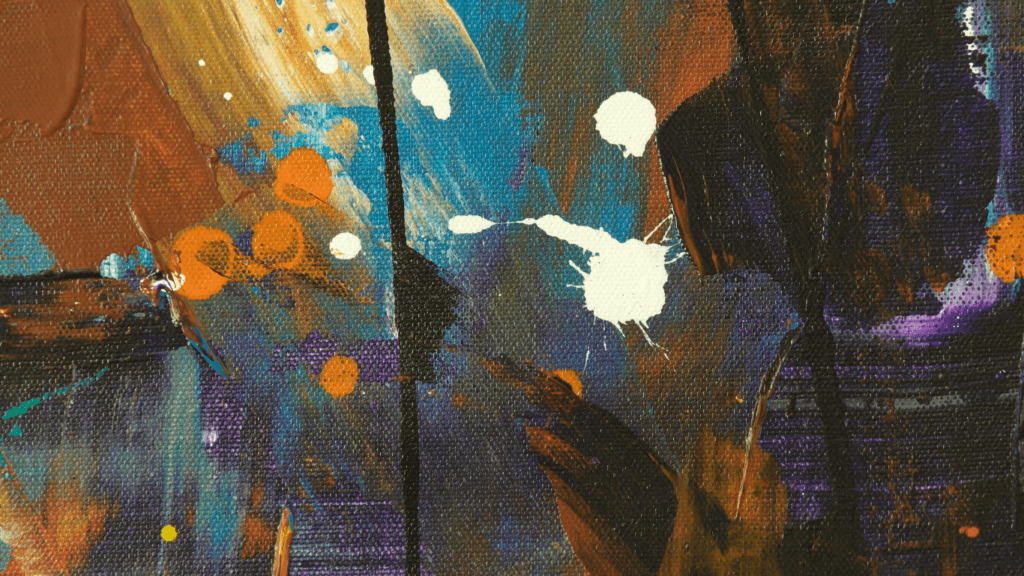Understanding Abstract Expressionism
Abstract Expressionism relies on emotion and spontaneity, making it a captivating yet complex art form. It’s essential to grasp its roots and features to fully appreciate it.
Origins and History
Abstract Expressionism emerged in the 1940s in New York City. Post-World War II, artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko broke away from traditional forms. Influenced by surrealism, they used abstraction to express subconscious thoughts. The movement highlighted individual perspective and emotional intensity, shifting the epicenter of the art world from Europe to the United States.
Key Characteristics
- Abstract Expressionist art often features large canvases and dynamic compositions.
- Brushstrokes are typically bold, creating a sense of movement.
- Colors range from stark contrasts to subtle gradations, enhancing the emotional impact.
- Two primary styles emerged: Action Painting and Color Field Painting.
- Action Painting, represented by Pollock, involves energetic applications of paint.
- Color Field Painting, championed by Rothko, focuses on large areas of a single color.
- Both styles emphasize personal expression and break from traditional representations.
Important Artists to Know
The Abstract Expressionist movement boasts several iconic figures whose works have left a lasting impact. Knowing these artists enhances your appreciation for this art form.
Jackson Pollock
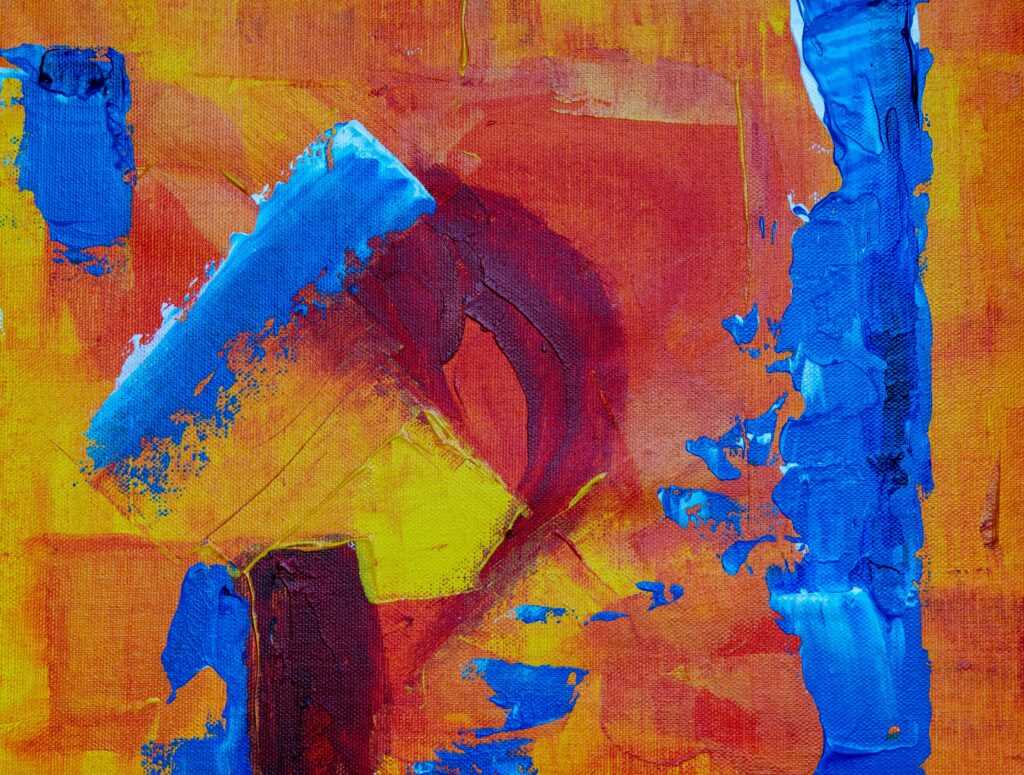
Jackson Pollock, a central figure in Abstract Expressionism, is renowned for his unique technique of drip painting. He abandoned traditional easel painting, opting to lay canvases on the floor and pour or splatter paint from above. This method brought a new level of dynamism and spontaneity to his works. “Number 1A, 1948” exemplifies Pollock’s use of layered drips and splashes. He emphasized the act of painting itself, making the process as significant as the finished piece.
Mark Rothko
Mark Rothko, another key Abstract Expressionist, focused on Color Field Painting. Unlike Pollock, Rothko’s works consist of large, floating rectangles of color that aim to evoke deep emotional responses. He sought to create a profound human experience through his paintings. “No. 61 (Rust and Blue)” showcases his signature style with soft, rectangular forms and layered colors. Rothko’s use of color and light created meditative spaces on canvas, inviting viewers to explore their inner emotions.
Techniques for Appreciating Abstract Art
When trying to appreciate abstract art, keep an open mind. Abstract Expressionism demands an experiential approach rather than a literal one.
Initial Impressions
Observe the artwork without preconceptions. Look for emotional cues in the colors, shapes, and composition. Note any immediate feelings or memories that the piece evokes. For instance, vibrant colors can symbolize joy, while darker shades might suggest melancholy.
Emotional Connection
Allow yourself to feel the emotions conveyed by the artist. Focus on how the artwork resonates with your own experiences. Artists like Jackson Pollock aimed to present subconscious thoughts, aiming to elicit strong emotional responses. Try to engage with the piece on a personal level, finding meaning in the emotions it stirs within you.
Interpretive Freedom
Embrace the lack of concrete meaning. Abstract Expressionism values personal interpretation. Compare your interpretations with those of others to gain new perspectives. For example, while one individual might see chaos in Pollock’s drip paintings, another might find harmony and movement. The freedom to interpret abstract art uniquely is what makes it so profound.
Tips for Newbies
Understanding Abstract Expressionist art can be challenging for newcomers. These tips will help deepen your appreciation and make your experience more rewarding.
Visit Museums and Galleries

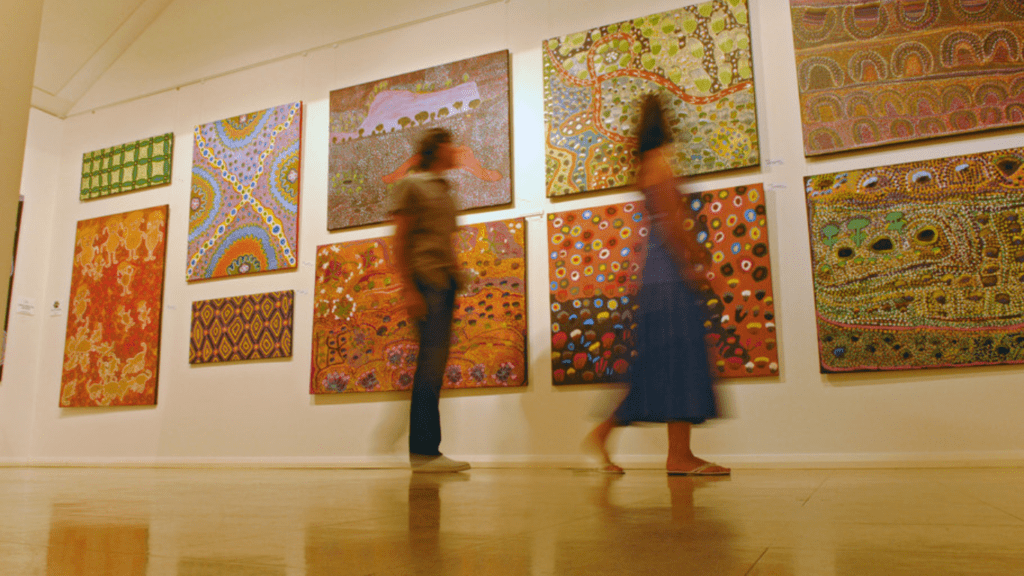
Explore local museums and galleries featuring Abstract Expressionist works. Seeing the art in person allows you to appreciate the scale, texture, and color nuances that digital images can’t convey. Institutions like the Museum of Modern Art in New York showcase extensive collections of works by key artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko.
Engage with Art Communities
Join art communities online or in person to discuss and explore Abstract Expressionist art. Forums and local art groups offer diverse perspectives and insights, enriching your understanding. Platforms like Reddit’s r/Art or local art society meetups can connect you with enthusiasts and experts alike.
Read and Research
Dive into literature on Abstract Expressionism to understand its historical context and artistic philosophies. Books like “Abstract Expressionism” by David Anfam provide in-depth analyses of the movement. Additionally, read articles from trusted art historians and critics to gain varied viewpoints and deepen your knowledge.
Overcoming Challenges
Appreciating Abstract Expressionist art can be challenging for newbies, but understanding common misconceptions and developing a personal perspective can make it easier.
Common Misconceptions
- Many believe Abstract Expressionism is chaotic or meaningless.
- The artworks might appear spontaneous, they embody deep emotional and philosophical significance.
- Novices often think they need to “get” the art immediately; this isn’t true.
- Over time and with increased exposure, recognizing the layers and intent behind the works becomes more intuitive.
- A widespread misconception is that Abstract Expressionist art lacks skill.
- Artists like Jackson Pollock and Mark Rothko followed precise techniques and sought to evoke emotions through their styles.
- It’s crucial to note that mastery and control guided even the seemingly unstructured elements.
Developing Your Perspective
Engaging actively with artworks will help in forming a unique perspective. Spend time observing a piece before moving on. Consider the artist’s historical context and emotions—these factors greatly influence interpretation.
Read artist statements or critique articles to gather varied viewpoints. This practice provides deeper insight into the meaning and significance behind the colors, shapes, and forms. Journaling your reflections on different pieces can track your evolving appreciation and understanding.
Interacting with others’ interpretations in art communities, both online and offline, can also expand your perspective. Discussions might reveal aspects you hadn’t considered, enriching your overall experience.